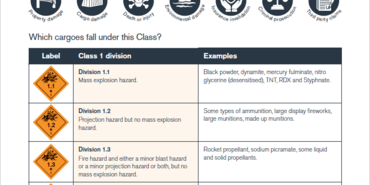
Dangerous goods quick reference guide - Class 2: Gases
Classification:
Gases are divided into three divisions:
2.1 Flammable Gases: Ignite in air or contribute to fire; sensitive to temperature changes.
Examples: Acetylene, butane, propane, LPG, hydrogen, aerosols.
2.2 Non-Flammable, Non-Toxic Gases: Can cause asphyxiation, oxidization, or explode under pressure.
Examples: Carbon dioxide, helium, nitrogen, oxygen, argon.
2.3 Toxic Gases: Harmful or fatal if inhaled.
Examples:
Chlorine, fluorine, methyl bromide, hydrogen fluoride, sulphur dioxide.
Key Handling Guidelines:
- Packing: Use tanks/cylinders per manufacturer’s instructions; never use damaged or overfilled containers; do not repackage without expert advice.
- Storing: Store in well-ventilated, temperature-controlled areas; keep away from heat sources; use leak detectors; inspect regularly; train staff in emergency response.
- Transporting: Ensure ventilation during transport; secure tanks/cylinders tightly; avoid ignition sources near flammable gases; have a security plan for high-consequence cargo; comply with CTU Code.
Handling:
Never throw, drop, or drag cargo; maintain emergency response plans; communicate clearly across the supply chain.
Documents
Dangerous Goods - Class 2 (151 kB) 11/12/2025
- Date
- 11/12/2025