CTU Code
The CTU Code Quick Guide, published by the Cargo Integrity Group, serves as an essential resource for safely packing cargo transport units (CTUs) across global supply chains. This comprehensive guide addresses critical safety protocols that prevent billions in annual losses from improper packing practices whilst ensuring compliance with the IMO/ILO/UNECE Code of Practice.
The guide systematically covers stakeholder responsibilities throughout the supply chain, from initial planning through final delivery. Key sections detail CTU condition checks, dangerous goods handling, and securing techniques essential for preventing cargo damage during multimodal transport. For transport & logistics operators, understanding these requirements proves vital for maintaining operational efficiency and reducing liability exposure.
Preventing contamination and ensuring compliance
The guide emphasises pest prevention measures, requiring ISPM-15 compliant timber and thorough contamination checks. All CTUs must undergo rigorous inspection for soil, insects, and animal contamination before packing commences. These measures protect agricultural resources whilst ensuring shipments meet international phytosanitary requirements.
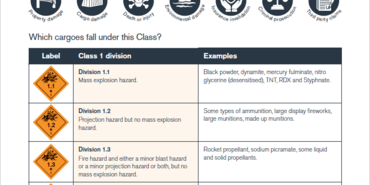
Proper securing methods receive extensive coverage, including specific guidance for heavy machinery, high centre-of-gravity items, and dangerous goods segregation. The document stresses that cargo handling facilities must implement systematic packing plans, utilising appropriate blocking, bracing, and lashing techniques to prevent cargo movement during transport.
Critical safety protocols include enclosed space entry procedures, recognising atmospheric hazards from previous cargoes or fumigation. The guide mandates proper ventilation and testing before entry, with specific requirements for monitoring personnel and emergency response procedures. Upon completion, packers must verify gross mass, affix ISO17712-compliant seals, and provide comprehensive documentation including Verified Gross Mass for maritime transport.
The comprehensive checklist ensures systematic compliance across thirty-four critical checkpoints, supporting effective claims management through proper documentation and procedure adherence.
Key takeaways
- Poor CTU packing practices cost the transport industry over US$6 billion annually
- All timber materials must meet ISPM-15 standards to prevent pest contamination
- Heavy cargo requires specific load distribution across CTU structural components
- Dangerous goods segregation follows strict IMDG Code requirements
- Verified Gross Mass documentation is mandatory for maritime container transport
- CSC Safety Approval Plates must be valid before CTU usage
- Fumigated units require Class 9 dangerous goods placarding and warning signs
Frequently asked questions
What is the maximum acceptable void space in a tight stow?
The cumulative void spaces in any horizontal direction should not exceed 15cm. Gaps exceeding this must be filled with appropriate dunnage or blocking materials to prevent cargo movement.
When should pest contamination authorities be contacted?
Contact your National Plant Protection Organisation immediately upon discovering plant-related contamination, or the Animal Quarantine Office for animal-origin contamination during CTU inspection.
What documentation is required for dangerous goods in CTUs?
Shippers must provide a Shipper's Declaration, and where required, a Packing Certificate declaration. Safety Data Sheets should be provided in hard copy for inland transport by road, rail, or waterway.
Documents
CTU Code: A Quick Guide - 2022 update (2.03 MB) 19/08/2022
CTU Code Checklist English (912 kB) 07/07/2023
CTU Code: A Quick Guide - Russian (2.83 MB) 25/10/2022
CTU Code: Interactive Checklist - Russian (878 kB) 20/10/2022
Code CTU Checklist French (866 kB) 19/10/2023
CTU Code: A Quick Guide French (1.96 MB) 24/11/2023
CTU Code Checklist simplified Chinese (0.91 MB) 19/10/2023
CTU Code: A Quick Guide simplified Chinese (2.18 MB) 28/07/2023
CTU Code Checklist traditional Chinese (0.90 MB) 19/10/2023
CTU Code - a quick guide - Trad Chinese (2.20 MB) 28/07/2023
CTU Code Checklist Italian (877 kB) 19/10/2023
CTU Code : A Quick Guide - Italian (2.03 MB) 15/08/2023
Código UTC Guía Español Agosto 2023 (1.99 MB) 05/09/2023
Código CTU Lista Español Agosto 2023 (866 kB) 23/11/2023
CTU Code: A Quick Guide - Arabic (1.57 MB) 30/11/2023
CTU Code Checklist Arabic (260 kB) 15/11/2023
- Author
- Staff Author
- Date
- 01/09/2022